The Connections section allows you to create,
edit, and delete connection profiles. The center box displays a list
of currently available profiles, together with a history of
connections that were made without being stored in a profile. You
can collapse or expand both the Connections and
History trees by double-clicking them.
Connections are automatically added to the
History tree whenever you establish a connection
to a MySQL server without using one of the profiles stored under the
Connections tree. They do not appear in the
drop-down box of the Connection dialog, but you
can use any of them by manually typing their name into the
Connection box of the
Connection dialog.
To edit an existing connection profile, click on its name and change
the values that appear in the Connection
Parameters and Advanced Parameters
tabs, then click on the Apply Changes button
to save your changes.
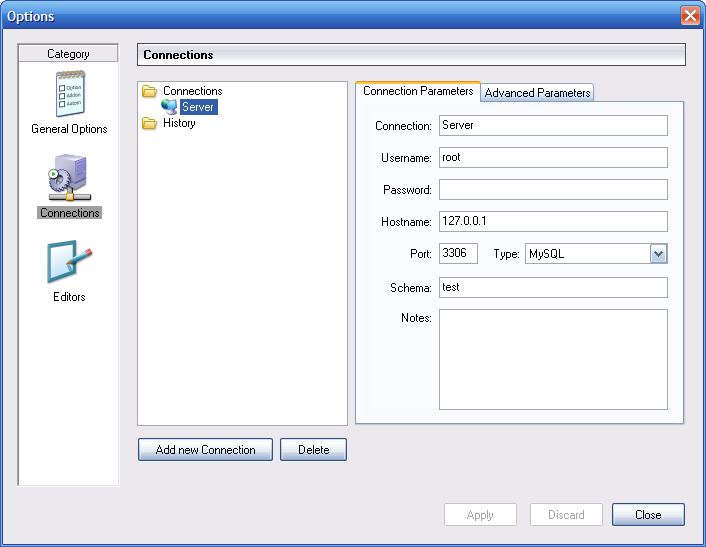
When you select a connection profile from either the
Connections or History trees,
the Connection Parameters tab displays the
following fields:
Connection: The connection profile label. This is the name by which you refer to the profile and that appears in theConnectiondrop-down box of the Connection dialog. It may contain any characters, including spaces. Choose distinctive names so that you can easily tell which profiles they refer to. The names can help you distinguish connections to different MySQL servers, or connections as different MySQL users to a given server.Username: The username used to connect to the MySQL server.Password: The password used to connect to the MySQL server. Note that passwords are not stored in the connection profile, unless you specify otherwise in the General Options section.Hostname: The name of the host machine where the MySQL server runs, or its IP address.Port: The TCP/IP port that the MySQL server listens to on the host machine.Type: Specifies the protocol used to connect to the database server. The default protocol isMySQL(which uses the native MySQL protocol).Schema: The default database for a connection when using the MySQL Query Browser.Notes: You can use this field to enter comments or additional information describing the connection profile.
Примітка
The Advanced Parameters tab is not available on
all platforms. Advanced parameters can still be configured in the
Connection dialog. Use the Details ...
button to display the Advanced Connection
Options.
When you select a connection profile from either the
Connections or History list,
the Advanced Parameters tab displays the
following checkboxes:
Use compressed protocol: If checked, the communication between the application and the MySQL server will be compressed, which may increase transfer rates. This corresponds to starting a MySQL command-line tool with the--compressoption.Return number of found rows, not number of affected rows: By default, MySQL returns the number of rows changed by the lastUPDATE, deleted by the lastDELETEor inserted by the lastINSERTstatement. When this option is checked, the server returns the number of rows matched by theWHEREstatement forUPDATEstatements.-
Ignore spaces after function names, make them reserved words: Normally, any reference to a function name in an SQL statement must be followed immediately by an opening parenthesis. If this option is checked, spaces may appear between the function name and the parenthesis, like this:COUNT (*)
Enabling this option has the effect that function names become reserved words. This option corresponds to starting a MySQL command-line tool with the
--ignore-spacesoption. Allow interactive_timeout seconds of inactivity before disconnect: Normally, the connection is closed by the MySQL server after a certain period of inactivity on the client side. This period can be set with theinteractive_timeoutvariable. If checked, the server will not close the connection unless the period of inactivity exceeds the value set byinteractive_timeout. This corresponds to starting a MySQL command-line tool with the--connect-timeout=option.secondsEnable LOAD DATA LOCAL handling: By default, theLOCALoption of theLOAD DATAstatement is disabled for security reasons. Enabling this option will allow you to load data from the local machine (the machine where the client GUI application is running). This option corresponds to starting a MySQL command-line tool with the--local-infile=1option. (Note that this option is ineffective unless the MySQL server allowsLOCALhandling.)
This is a translation of the MySQL Administrator Manual that can be found at dev.mysql.com. The original MySQL Administrator Manual is in English, and this translation is not necessarily as up to date as the English version. Даний документ є перекладом оригінальної англійської документації по MySQL Administrator яка доступна за адресою dev.mysql.com .